UI vs. UX: Key Differences for Success
Discover the key differences between UI and UX design and explore which career path may suit you best.

In the tech world, terms like User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) often come up, sometimes used interchangeably. However, these two fields are distinct in many ways. So, what exactly do UI and UX mean? And what does it take to become a UI or UX designer?
In this article, we’ll explore the similarities and differences between UX designers and UI designers, helping you understand their distinct roles. We’ll also guide you on how to decide which path may be right for you. Lastly, we’ll provide tips on how to get started in either field, even if you don’t have a degree or prior experience.
UI vs. UX: What Sets Them Apart?
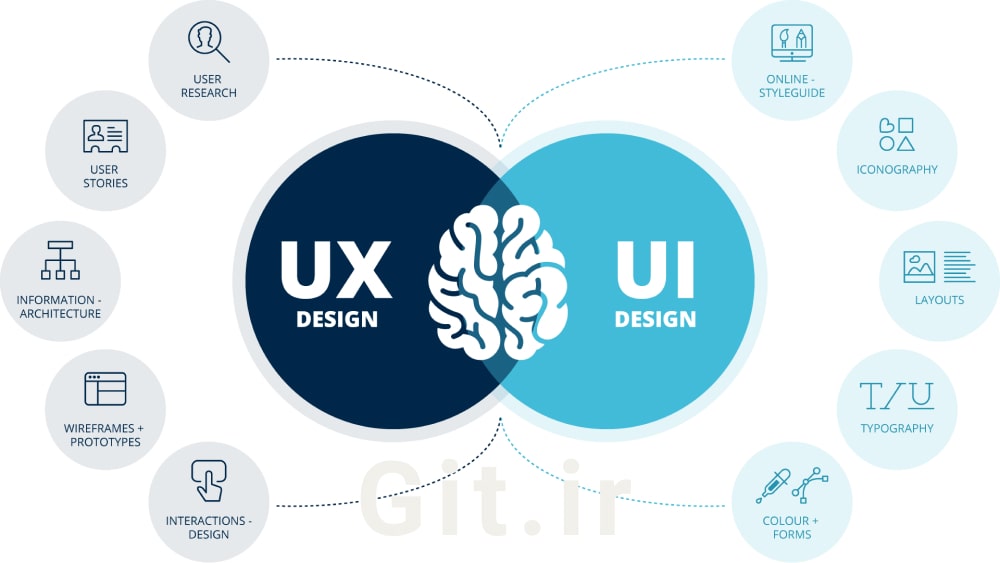
UI (User Interface) involves the visual elements you engage with when using a website, app, or any other digital platform. This includes everything from screens and buttons to toggles and icons. UX (User Experience), on the other hand, focuses on the entire interaction you have with a product-how it works and how you feel while using it. Though UI can influence UX, they serve different purposes, as do the roles of UI and UX designers.
Creating a successful product often requires both strong UI and UX. For instance, a banking app may have an appealing design and easy-to-use navigation (UI), but if the app is slow or makes transferring money complicated (UX), its good looks won’t matter-you likely won’t continue using it.
Similarly, a website might offer valuable, well-organized content, but if its design feels outdated or the navigation is confusing, you’re more likely to leave the site.
Roles and Responsibilities: What Do UI and UX Designers Do?
Both UI and UX designers are essential throughout the product development process. Here’s a closer look at their unique responsibilities.
UX designers focus on shaping the overall experience a user has with a product. Their aim is to design products that are not only functional but also accessible and enjoyable to use. Although UX is typically associated with digital products, it can extend to non-digital experiences as well, like using a coffee machine or navigating a public transportation system. Key tasks for UX designers often include:
Conducting user research to uncover the goals, needs, behaviors, and frustrations users face when interacting with a product
Creating user personas that represent target customers
Mapping user journeys to understand how customers engage with the product
Building wireframes and prototypes to refine the product’s design
Running user tests to validate design choices and spot potential issues
Collaborating with stakeholders, UI designers, and developers
Learn more: What Does a UX Designer Do?
UI designers are responsible for designing the graphical elements of mobile apps, websites, and digital devices—the parts that users directly interact with. Unlike UX, which can apply to both digital and non-digital products, UI is specifically focused on digital interfaces. A UI designer’s goal is to create designs that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive and easy to navigate. Typical tasks for UI designers include:
Structuring page layouts for clear organization
Selecting color schemes and typography that enhance the design
Designing interactive features such as buttons, toggles, drop-down menus, sliders, and text fields
Producing high-fidelity wireframes and layouts that represent the final design
Collaborating closely with developers to bring the design to life
Learn more: What Is a User Interface (UI) Designer?
Is There a Role for UI/UX Designers?
When you search for UX positions on job listing sites, you’ll often come across companies seeking UI/UX designers. Some organizations do look for candidates who possess skills in both areas. However, upon closer inspection of these job listings, you may find that the roles often favor one focus over the other.
As you start your job search, it’s essential to pay more attention to the specific tasks and qualifications listed rather than getting caught up in the job title itself.
Skills
While UI and UX designers share some overlapping skills, each position also demands a distinct skill set.
Education
While a degree isn’t always required to land a job as a UX or UI designer, having one can certainly enhance your job prospects. Only a limited number of universities offer specialized programs in UI/UX design. UX designers often hold degrees in fields such as computer science, psychology, human-computer interaction, or general design. In contrast, UI designers typically graduate with degrees in digital design, graphic design, or interaction design.
Salary
As reported by Glassdoor, the average salary for UX designers in the United States, including base pay and additional earnings like commissions and bonuses, is approximately $94,260. For UI designers, this figure averages around $98,758. Your salary may vary based on several factors, including your location, the industry you work in, your level of experience, and your educational qualifications.
How to Identify If UI or UX Design Suits You Better
Both UI and UX design are lucrative and in-demand career paths. The choice between the two largely depends on your personal interests and career goals. If you have a passion for technology, enjoy variety, and excel at problem-solving, user experience design could be a great fit for you. Alternatively, if you have a creative mindset and a keen eye for aesthetics, user interface design may be the path to consider.
If you’re still uncertain about which direction to take, here are some ways to explore your options:
Take Courses: Enroll in classes for both UI and UX to gain hands-on experience in each area.
Follow Industry Experts: Read articles or listen to podcasts focused on UI/UX to learn from professionals in the field.
Network: Connect with industry experts on LinkedIn and request informational interviews to gain insights.
Join Design Communities: Participate in online design forums where you can ask questions and engage with others in the field.
Other Roles in User Experience
The field of UX encompasses more than just UI and UX designers. If you’re considering a career in UI/UX, you might also want to explore these related roles:
UX Researchers: These professionals investigate the goals, needs, desires, and challenges of both existing and potential users of a product.
UX Writers: They craft the text found on websites, apps, and other digital platforms, ensuring clarity and consistency in messaging.
Interaction Designers: Focused on the overall user interaction with digital products, interaction designers consider how users engage with interfaces in a comprehensive manner.
Developers: These individuals take the designs created by UI and UX designers and turn them into functional software, websites, or applications through coding.
Product Designers: They oversee the entire process of transforming a product or service from concept to reality, coordinating various aspects of design and development.
Content Strategists: Responsible for planning and managing marketing content, content strategists ensure that messaging aligns with the project’s lifecycle and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between UX and UI design?
UX design focuses on the overall experience a user has with a product, aiming to make it functional and enjoyable. UI design, on the other hand, is about the visual elements that users interact with, such as buttons, icons, and layouts. Both play important roles in creating a successful product.
Why is research important in UX/UI design?
Research is vital because it helps designers understand users’ needs and behaviors. By gathering data through surveys, interviews, and usability tests, designers can make informed decisions that enhance the user experience.
Can I be a UX/UI designer without a degree?
Yes! While having a degree can be beneficial, many successful designers come from diverse backgrounds. Building a strong portfolio and gaining relevant experience through projects and courses can be just as important.
How can I get started in UX/UI design?
You can start by taking online courses, reading design-related books, and practicing your skills on personal projects. Joining design communities and seeking feedback can also help you grow and learn from others.
What tools do UX/UI designers use?
Designers often use tools like Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch, and InVision for creating wireframes and prototypes. They may also use usability testing tools to gather feedback on their designs.
What skills do I need to succeed in UX/UI design?
Key skills include strong communication, problem-solving, and empathy for users. Familiarity with design software, understanding design principles, and the ability to conduct user research are also essential.
Please Log in to leave a comment.